Pipe Nipples
Stainless Steel Pipe Nipples
Black Steel Pipe Nipples
Galvanized Pipe Nipples
King Nipples
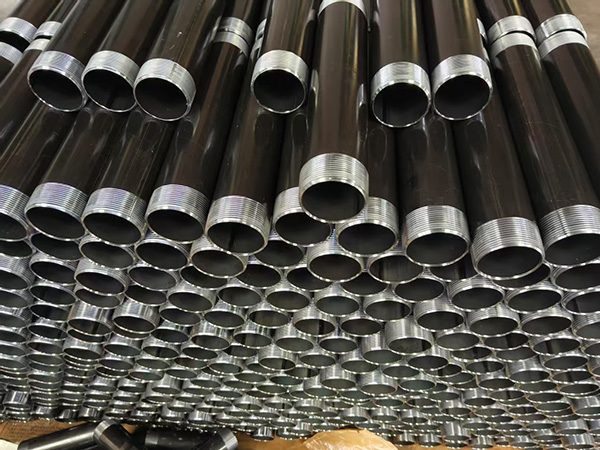

Oil Pipe
"Oil pipe"refers to pipes specifically designed for the transportation of oil,including crude oil,refined petroleum products,and natural gas.These pipes are critical components in the oil and gas industry,ensuring the safe and efficient movement of fluids over long distances.Below is an overview of oil pipes,including their types,materials,standards,and applications:
1.Types of Oil Pipes
Oil pipes can be categorized based on their manufacturing process and application:
By Manufacturing Process:
Seamless Pipes:Made without welding seams,offering higher strength and reliability for high-pressure applications.
Welded Pipes:Created by welding steel plates or coils,commonly used for low to medium-pressure applications.
Longitudinal Welded Pipes:Welded along the length of the pipe.
Spiral Welded Pipes:Welded in a spiral pattern,often used for large-diameter pipelines.
By Application:
Line Pipes:Used for transporting oil and gas over long distances,both onshore and offshore.
Casing Pipes:Used in oil wells to stabilize the wellbore and prevent collapse.
Tubing Pipes:Used inside casing pipes to extract oil and gas from the well.
Drill Pipes:Used in drilling operations to transmit drilling fluid and torque.
2.Materials
Oil pipes are typically made from high-strength materials to withstand harsh conditions,including high pressure,corrosion,and extreme temperatures.Common materials include:
Carbon Steel:Widely used due to its strength and affordability.
Alloy Steel:Enhanced with elements like chromium,nickel,or molybdenum for improved corrosion resistance and strength.
Stainless Steel:Used in highly corrosive environments.
Duplex Steel:Combines high strength and excellent corrosion resistance,often used in offshore applications.
3.Standards
Oil pipes must meet specific industry standards to ensure safety and performance.Common standards include:
API 5L:Specifies requirements for seamless and welded steel pipes used in pipeline transportation systems for oil and gas.
ASTM A106:Covers seamless carbon steel pipes for high-temperature service.
ASTM A53:Covers seamless and welded black and galvanized steel pipes for general use.
ISO 3183:International standard for steel pipes used in pipeline transportation systems.
4.Key Features
High Strength:Designed to withstand high internal and external pressures.
Corrosion Resistance:Often coated or treated to resist corrosion caused by oil,gas,and environmental factors.
Durability:Built to last in harsh environments,including offshore and subsea applications.
Weldability:Easy to join and install in pipeline systems.
5.Applications
Oil pipes are used in various stages of oil and gas operations:
Exploration:Drill pipes and casing pipes are used during drilling.
Production:Tubing pipes are used to extract oil and gas from wells.
Transportation:Line pipes are used to transport oil and gas from production sites to refineries or distribution centers.
Refining and Distribution:Pipes are used in refineries and distribution networks to move refined products.
6.Surface Treatments and Coatings
To enhance performance and longevity,oil pipes often undergo surface treatments:
External Coatings:Such as epoxy,polyethylene,or fusion-bonded epoxy(FBE)to protect against corrosion and environmental damage.
Internal Coatings:Used to reduce friction and prevent corrosion from transported fluids.
Cathodic Protection:An electrochemical method used to prevent corrosion in buried or submerged pipelines.
7.Market and Industry
Oil pipes are a critical component of the global energy infrastructure.The demand for oil pipes is driven by:
Oil and Gas Exploration:Especially in remote or offshore locations.
Pipeline Projects:Large-scale projects for transporting oil and gas across regions.
Maintenance and Replacement:Aging pipelines require regular maintenance or replacement.
8.Selection Considerations
When choosing oil pipes,consider the following factors:
Operating Pressure and Temperature:Ensure the pipe can handle the required conditions.
Environmental Conditions:Consider factors like soil type,water exposure,and climate.
Regulatory Compliance:Ensure the pipes meet local and international standards.
Cost and Availability:Balance performance requirements with budget constraints.
If you have specific requirements or need further assistance(e.g.,procurement,technical specifications),consulting with a professional supplier or manufacturer is recommended to ensure the right product for your application.
What should I do if the stainless steel joint leaks?
Stainless steel joints are a common type of pipeline connection,which are widely used in in ...
2025-01-07
Several common problems in the use of stainless steel joints
With the continuous development of stainless steel joint technology and enterprises, stainl ...
2025-01-07
How to deal with the phenomenon of stainless steel joints shining?
A simple stainless steel joint is dipped in toothpaste or vinegar with a cotton cloth, and ...
2025-01-07
How is the hardness of stainless steel threaded fittings measured?
Stainless steel threaded fittings are generally measured by three hardness indicators:Brine ...
2025-01-07